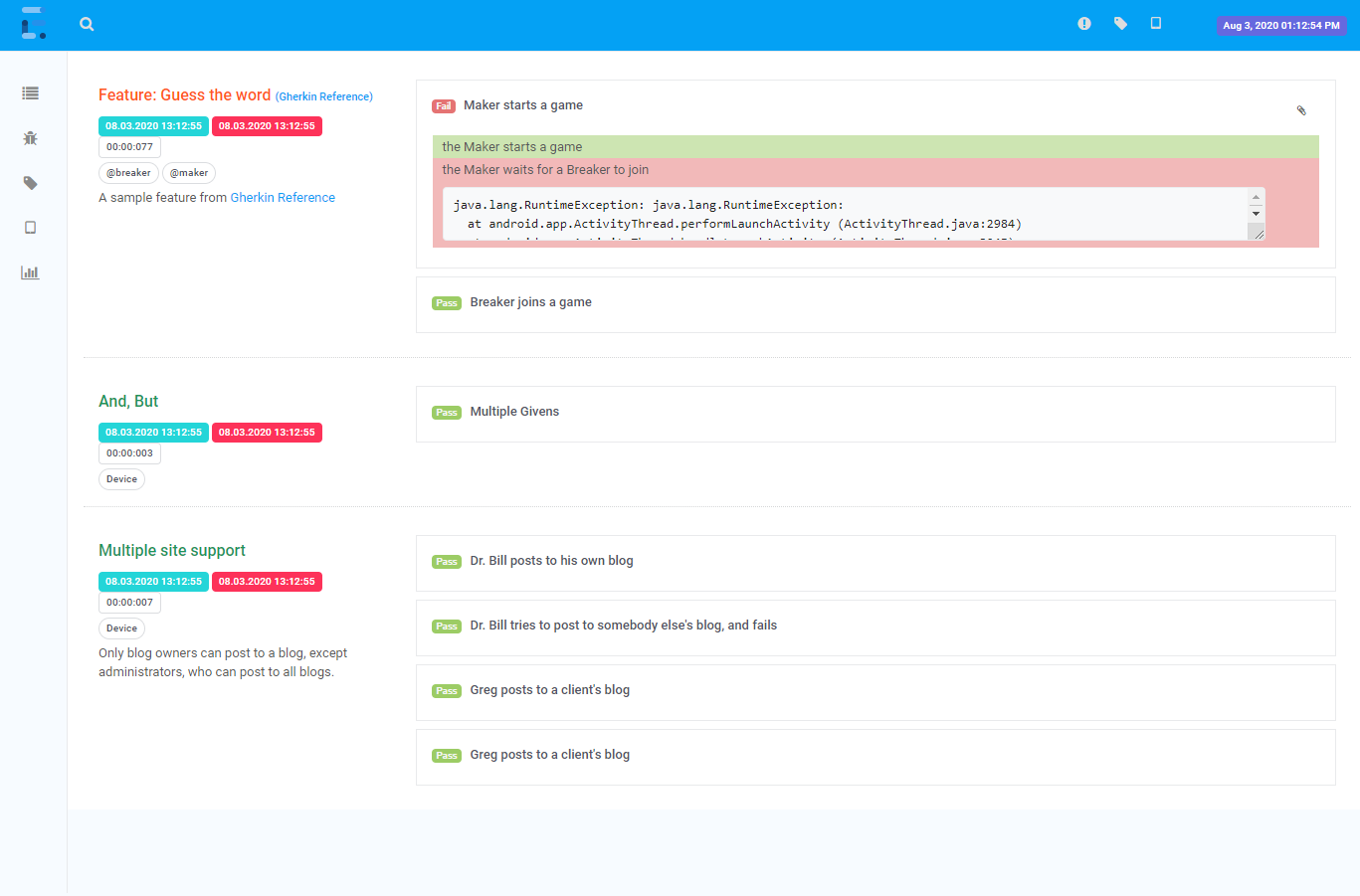
Extent reports are an essential part of test automation that allows testers to generate detailed reports of their test results. These reports provide valuable insights into the application’s performance under test and help identify any issues that may have arisen during the testing process. Extent reports are widely used in the industry and are supported by popular test automation frameworks like Selenium.
One of the key features of Extent Reports in Selenium is their ability to provide a comprehensive view of the test results. They allow testers to view the results of individual test cases and the overall status of the test suite. This makes it easy to identify failed tests and quickly pinpoint the root cause of the issue.
Another advantage of Extent reports is their flexibility. They can be customized to meet the project’s specific needs and can be integrated with other tools to provide a seamless testing experience. Overall, Extent reports are an indispensable tool for any test automation project that values detailed reporting and analysis of test results.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Reporting Matters in Selenium Test Automation
In Selenium-based test automation, reporting isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a necessity. Well-structured reports serve as the bridge between testers, developers, and business stakeholders. By transforming raw test data into clear, actionable summaries, they ensure everyone can easily understand the health and stability of the application.
Comprehensive reports highlight which tests passed, failed, and where problems may have occurred. This visibility is vital for quickly isolating issues, tracking regressions, and ultimately supporting faster releases with higher confidence. Plus, visually rich reports, like those generated by Extent Reports, make it easy to spot trends or anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Getting Started with Extent Reports
Extent Reports is a popular Java library that generates interactive and customizable test reports. This section will cover the basic steps to set up and create your first test report using Extent Reports.
Setting Up Automation Reporting
To use Automation Reporting in your Java project, add the Extent Reports dependency to your project’s pom.xml file. You can do this by adding the following code to the dependencies section of your pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aventstack</groupId>
<artifactId>extentreports</artifactId>
<version>5.0.6</version>
</dependency>
Once you have added the dependency, you can create an instance of the ExtentReports class in your test code to start generating reports.
Creating Your First Test Automation Reports
To create Test Automation Reports with Extent Reports, you need to create an instance of the ExtentTest class and add test steps to it. You can add test steps using the createTest
class method.
ExtentReports extent = new ExtentReports(); ExtentTest test = extent.createTest("My First Test", "This is a sample test"); test.pass("Step 1: Launch the browser"); test.pass("Step 2: Navigate to the website"); test.pass("Step 3: Enter username and password"); test.fail("Step 4: Verify login functionality"); extent.flush();
In the above code, we first create an instance of the ExtentReports class and then create an instance of the ExtentTest class using the createTest method. We then add test steps to the test using the pass and fail methods of the ExtentTest class. Finally, we call the flush method of the ExtentReports class to generate the report.
How Extent Reports Compare to Default TestNG Reports
While TestNG includes built-in reporting features, these are typically more basic in both presentation and detail. The default TestNG reports primarily offer a textual summary of test executions, showing which tests passed or failed, without much visual flair or the ability to dig deeper into each step.
By contrast, Extent Reports provide a much richer and more interactive experience. With Extent Reports, you can view colorful charts, expandable logs, and even embed screenshots for failed steps, making spotting patterns and troubleshooting issues easier. This additional layer of detail and customization is especially valuable when tracking large or complex test suites, where quick insight into failures and trends can save significant debugging time.
In short, if you’re looking for a reporting tool that goes beyond just the basics and helps you visualize and communicate your test results, Extent Reports offer a significant upgrade over the simple summaries generated by TestNG.
Major Components of Extent Reports
Extent Reports comprises two primary classes:
- ExtentReports Class
- Purpose: This class is responsible for generating HTML reports.
- Arguments: It accepts two arguments: the file path for report generation and a boolean indicating whether to overwrite existing data. Overwriting is enabled by default.
- Methods:
flush: Clears any previous data from memory and writes the final report to the output file.
- ExtentTest Class
- Purpose: This class is used to log each test step, helping track the progress and results of the test cases.
- Methods:
startTest: Used to execute preconditions of a test case.endTest: Used to execute postconditions of a test case.log: Logs the status of each step, whether passed or failed.
Logging Test Steps and Results
With Extent Reports, you can log various test outcomes to provide detailed feedback in your report. The log() method of the ExtentTest class accepts two arguments: the test status and a message to display in the report. Supported statuses include:
- PASS: Indicates a successful test step.
- FAIL: Indicates a failed test step.
- SKIP: Marks a test step as skipped.
- INFO: Provides informational messages.
Example usage:
test.log(LogStatus.PASS, "Test Passed");
test.log(LogStatus.FAIL, "Test Failed");
test.log(LogStatus.SKIP, "Test Skipped");
test.log(LogStatus.INFO, "Test Info");
After logging your steps, ensure you call endTest(test) to wrap up the test and flush() to generate the final report. This level of detail in your reporting helps you quickly identify what went right—and what didn’t—throughout your automated test execution.
Enhancing Extent Reporting Selenium with Advanced Features
Extent Reports provides several advanced features to enhance the quality and usability of Extent Reporting Selenium. These features allow testers to add more information to their reports, customize the layout and style, and integrate them with different test frameworks.
Adding Screenshots and Logs
One of the most useful features of Extent Reports is the ability to add screenshots and logs to the test reports. Screenshots can be added to the report after each step or test case, making it easier to identify the issues. Logs can also be added to the report, providing more details about the test execution.
To enhance your reports, especially when a test fails, you can capture and include a screenshot using the following approach:
// Capture a screenshot when a test fails
File src = ((TakesScreenshot)driver).getScreenshotAs(OutputType.FILE);
String path = "screenshot.png";
FileUtils.copyFile(src, new File(path));
// Log the failure and attach the screenshot
test.log(LogStatus.FAIL, "Screenshot on failure: " + test.addScreenCapture(path));
This code snippet demonstrates how to use the TakesScreenshot Interface to grab a snapshot of the current browser state. By saving this image and attaching it to the test report, you improve the report’s clarity and streamline the debugging process.
The logging feature, achieved through test.log(LogStatus.FAIL, ...)Ensures that each failure is documented with contextual evidence, making it easier to pinpoint the root cause of the issue. Such detailed reports are invaluable for maintaining high-quality test standards and efficiently identifying and resolving errors.
Customizing Report Layout and Style
Extent Reports allows testers to customize the layout and style of the test reports. Testers can choose from themes and styles, add logos and images, and customize the report title and header. They can also customize the report layout by adding sections such as test steps, test case details, and charts.
Integrating with Test Frameworks
Extent Reports can be easily integrated with JUnit, NUnit, and TestNG Framework. Testers can generate Extent Reports in HTML and combine them with their test framework reports. This allows them to view all the test results in one place and analyze the test execution easily.
In addition, Extent Reports can also be integrated with Klov, a server application that provides historical test reports and analysis. This allows testers to view the test execution history and analyze the test results over time.
Overall, Extent Reports provides several advanced features to enhance the quality and usability of test reports. Testers can add screenshots and logs, customize the report layout and style, and integrate them with different test frameworks, making Extent Reports a powerful tool for test reporting and analysis.
Integrating Extent Reports with JUnit and TestNG
Integrating Extent Reports with popular testing frameworks like JUnit and TestNG is a straightforward process that enhances your testing workflow with interactive, detailed reports. Here’s how you can set up Extent Reports with these frameworks to streamline your automation reporting:
1. Add Extent Reports to Your Project
- Download the
extentreportslibrary (JAR file) and include it in your project’s build path. - If you’re using Maven or Gradle, you can add the relevant dependency to your
pom.xmlorbuild.gradlefor easier integration.
2. Initialize Extent Reports in Your Test Setup
- Create an instance of the
ExtentReportsclass at the start of your test execution. - Specify the output directory and file name where the HTML report will be stored.
- For example:
ExtentReports report = new ExtentReports("Path/to/your/report.html", true);
3. Use ExtentTest to Log Test Steps
- Create an An
ExtentTestobject for each test case or test class to log individual test steps. - This object tracks the progress, logs statuses like PASS, FAIL, and INFO, and attaches screenshots or custom logs as needed.
4. Annotate and Structure Test Methods
- With JUnit or TestNG, leverage annotations (e.g.,
@BeforeClass,@Test,@AfterClass) to control test flow:- In the setup methods (
@BeforeClassor@BeforeSuite), initialize the Extent Reports and ExtentTest objects. - Within each test (
@Test), run your automation steps and log results using thetest.log()method with appropriate statuses. - After each test or at the end (
@AfterClassor@AfterSuite), callendTest()andflush()to finalize the report and write it to disk.
- In the setup methods (
5. Generate and View the HTML Report
- Once tests are complete, you’ll find an HTML file at your designated location.
- When you open this file in a browser, you’ll see interactive charts, logs, and—if enabled—screenshots to help you analyze each test run.
6. Customizing and Integrating Further
- Extent Reports integrates smoothly with JUnit and TestNG through listeners and report hooks, allowing you to automate report generation further.
- You can merge Extent Reports with your existing test suite outputs or continuous integration pipelines for unified reporting.
By following these steps, you ensure that your automated test results are not only recorded but are also accessible, interactive, and much richer in detail than default framework reports. This dramatically simplifies debugging and overall test management, especially when teams adopt frameworks like JUnit, TestNG, or NUnit.
How to Generate Extent Reports in Selenium?
Creating detailed test reports is essential in any automated testing process. Extent Reports is a powerful library that helps you do just that with your Selenium projects. Here’s a concise guide to getting started.
Step 1: Add the Required Library
First, incorporate the extentreports-java library into your project. This involves adding the appropriate JAR file to your project’s build path.
Step 2: Set Up Your Java Class
Create a new Java class where you will write the logic for generating reports. Here’s an outline to help structure your code:
- Initialize Important Classes:
- Use
ExtentReportsto manage your report, andExtentTestfor individual test results.
- Use
- Set Up BeforeClass Method:
- Define a method annotated with
@BeforeClassto initialize the report and test objects. This configuration determines where your HTML report will be saved.
- Define a method annotated with
@BeforeClass
public static void setupReport() {
report = new ExtentReports(System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/ExtentReportResults.html");
test = report.startTest("Demo Test");
}
Step 3: Write Your Test Method
With JUnit annotations, configure a test method to automate your web actions.
- Launch a Browser: Initialize your WebDriver, set the Chrome driver path, and open a specified URL.
- Verify Page Title: Capture the title and compare it with the expected string. Log the result as a pass or fail.
@Test
public void validatePageTitle() {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "path/to/chromedriver");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://example.com/");
if (driver.getTitle().equals("Expected Title")) {
test.log(LogStatus.PASS, "Page title is correct.");
} else {
test.log(LogStatus.FAIL, "Page title is incorrect.");
}
driver.quit();
}
Step 4: End the Test and Generate Report
Finalize your report within an @AfterClass method. This involves ending each test and generating the report file.
@AfterClass
public static void teardownReport() {
report.endTest(test);
report.flush();
}
By following these steps, you can effectively generate comprehensive Extent Reports in your Selenium testing workflows. Adjust paths and configurations as necessary to fit your testing environment.
Analyzing Test Results
Understanding Test Outcomes
Once tests have been executed using Extent Reports, the next step is to analyze the results. This involves examining the status of each test, whether it passed, failed, or was skipped. The status of each test is represented by a pie chart that provides a visual representation of the overall outcome of the test suite.
The pie chart can be used to quickly identify which tests passed, which failed, and which were skipped. This information is useful for project stakeholders who need to know the status of the project and whether any issues need to be addressed.
Leveraging Reports for Project Insights
One of the advantages of using Extent Reports is that it provides project stakeholders with insights into the project. The reports can be used to identify trends and patterns in the test results, which can help project managers make informed decisions about the project.
Communicating and Tracking Defects Effectively
Extent Reports play a crucial role in communicating and tracking defects with stakeholders. By offering comprehensive and customizable reports, they facilitate clear communication channels, ensuring that stakeholders are well-informed about the project’s testing status. This level of detail helps in pinpointing defects, allowing teams to address issues promptly and efficiently.
For example, if a particular test consistently fails, it may indicate a problem with the application or the test itself. By identifying these issues early on, project managers can take corrective action to prevent them from becoming bigger problems later on.
Improving Testing Approaches and Resolution Speed
In addition to identifying issues, the reports can also be used to measure the effectiveness of the testing process. For example, if the number of failed tests decreases over time, it may indicate that the testing process is becoming more effective. Extent Reports not only highlight areas for improvement but also contribute to faster defect resolution, leading to more robust testing strategies.
Overall, Extent Reports provides project stakeholders with a clear and concise way to analyze test results. By leveraging the reports, project managers can make informed decisions about the project and ensure that it is on track to meet its goals. By enhancing communication and tracking, they ultimately lead to more efficient testing practices and quicker problem-solving, aligning the project with its objectives.t
Best Practices and Troubleshooting
Optimizing Report Generation
Generating reports can be a memory-intensive task, especially when dealing with large amounts of data. To optimize report generation, it is recommended to use the latest version of the extentreports-java library and allocate sufficient memory to the JVM.
Additionally, it is recommended to design your tests with report generation in mind. For example, avoid creating unnecessary objects or variables that could consume memory and slow down report generation.
Resolving Common Issues
When working with extent reports, it is important to be aware of common issues that may arise and how to resolve them.
One common issue is the NoClassDefFoundError error, which may occur when the extentreports-java-2.41.2.jar file is not properly included in the classpath. To resolve this issue, ensure that the jar file is included in the classpath and that the correct version is being used.
Another issue that may arise is related to debugging. When encountering issues with extent reports, it is recommended to enable debug mode to obtain more detailed information about the issue.
In terms of design, it is essential to ensure that tests are properly structured and organized to avoid issues with report generation. For example, avoid nesting tests within each other or using complex data structures that may cause issues with report generation.
Finally, to ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to periodically clean up old report files and avoid generating unnecessary reports.
By following these best practices and troubleshooting tips, users can optimize their experience with extent reports and avoid common issues.
| You May Also Be Interested to Know- | |
| 1. | Visual Testing |
| 2. | Benefits of Automation Testing |
| 3. | Cucumber Framework |