Table of Contents
ToggleTest Environment Management: Streamlining Testing Processes
What is Test Environment?
A Test Environment plays a vital role in software testing. It consists of pre-production or staging environments that closely resemble the production environment, albeit in a downgraded version. The purpose of a test environment is to simulate real-life scenarios and uncover any defects before the software is deployed to the production environment. Test environments are designed to provide a controlled space for testing activities without impacting live operations. The practice of testing in production has also emerged in recent years and in an interesting trend to watch.
Key Challenges in Test Environment Management
Effective Test Environment Management faces several challenges, which, if not addressed properly, can hinder the testing process and affect software quality. Let’s explore some of these challenges:
- Complex Infrastructure Dependencies: Managing intricate IT infrastructure dependencies can be a daunting task. As software systems become more interconnected, the need for manual intervention increases. This can lead to unorganized and ad-hoc management of environments, resulting in operational inefficiencies and higher maintenance costs.
- Environment-Related Defects: Identifying and resolving defects related to the test environment can be a significant concern for QA teams. Issues such as misconfiguration, incompatible software versions, or insufficient resources can lead to inaccurate test results and delay the testing process
- Test Data Management: Managing test data is crucial for comprehensive testing. Ensuring the availability of the right data sets, data privacy, and compliance with regulations pose additional challenges. TEMS should include provisions for efficient test data management to avoid bottlenecks in the testing process.
Automation Framework Test Environment for Software Testing
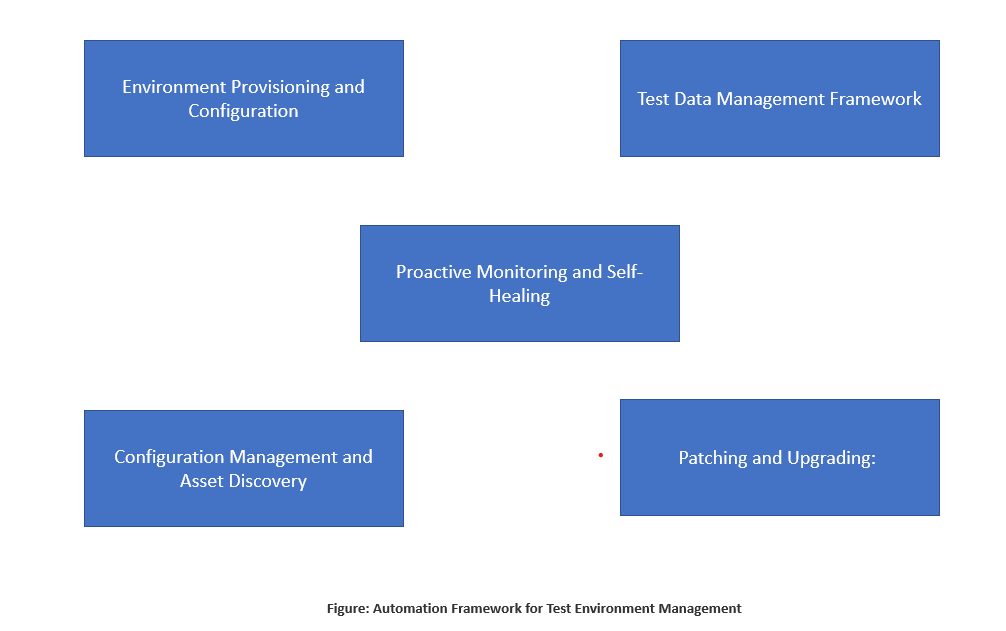
To overcome the challenges in Test Environment Management, organizations are adopting automation frameworks within their DevOps lifecycles. An automation framework enables the automation of various tasks related to environment management, ensuring efficiency and reliability. Key areas covered by an automation framework include:
- Environment Provisioning and Configuration: Automation streamlines the process of setting up and configuring environments. It enables quick and accurate provisioning of necessary hardware, software, and network configurations required for testing.
- Test Data Management: Automation frameworks help manage test data efficiently. They provide mechanisms for generating, anonymizing, and securely storing test data, ensuring data privacy and compliance.
- Proactive Monitoring and Self-Healing: Automation allows for real-time monitoring of environments. It enables the detection of issues or performance bottlenecks and provides automated self-healing capabilities to resolve recurring incidents.
- Configuration Management and Asset Discovery: Automation frameworks facilitate configuration management by automatically discovering environment assets and managing to license. This ensures accurate and up-to-date configuration information for the environments.
- Patching and Upgrading: Automation streamlines the process of patching and upgrading infrastructure components within the test environment. This ensures compliance with enterprise policies and reduces the risk of vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Test Environment for Software Testing
Implementing effective Test Environment for Software Testing management offers numerous benefits for organizations:
- Error Reduction and Timely Testing: Automation minimizes errors caused by manual interventions and reduces delays due to complex dependencies. It enables testing teams to access the required environments promptly, ensuring the timely execution of test cases.
- Continuous Availability: QA environments are crucial for ongoing development and testing activities. With efficient management, organizations can maintain the continuous availability of test environments, allowing teams to work seamlessly without disruptions.
- Consistent and Accurate Environments: Automation ensures consistent and accurate test environments through automated configuration updates. This reduces the risk of misconfigurations and provides reliable testing results.
Optimal Resource Utilization: QA environment management automation optimizes the utilization of infrastructure assets. It enables better license management, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Environment as a Service: Implementing a robust environment management framework enables organizations to provide environments as a service. This self-service model empowers development and testing teams to request and provision the required environments independently, reducing dependency on IT teams and streamlining the overall process.
In conclusion, test environment management plays a crucial role in the success of software testing. Overcoming challenges through automation and implementing an efficient framework provides organizations with numerous benefits, including streamlined testing processes, improved software quality, and optimized resource utilization. By investing in test environment management, organizations can ensure the smooth execution of their testing activities and deliver high-quality software products to their customers.
| You May Also Be Interested to Know- | |
| 1. | Test Case Design |
| 2. | Software Development Engineer Test |
| 3. | Automation Reporting |
FAQ on Test Environment Management
Q: How do you effectively balance the cost and complexity of maintaining multiple test environments against the benefits they provide?
A: Balancing the cost and complexity of maintaining multiple test environments while maximizing their benefits is a common concern for many organizations. The key is to adopt a strategic approach that emphasizes optimization and efficiency. Start by evaluating the specific needs of your projects and aligning them with the right mix of test environments. This involves identifying the minimum set of environments necessary to cover your testing needs without unnecessary duplication. Leverage virtualization and cloud technologies to create scalable and on-demand environments that can be spun up as needed and decommissioned when not in use, reducing both costs and maintenance overhead. Implementing infrastructure as code (IaC) can also streamline the setup and tear-down process, ensuring consistency and reducing manual effort. Additionally, consider the use of shared environments for non-conflicting tests to maximize resource utilization. Regularly review and rationalize your test environments to ensure they continue to meet your needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
Q: What specific metrics or KPIs should organizations track to assess the effectiveness of their Test Environment Management practices?
A: To assess the effectiveness of Test Environment Management practices, organizations should track a variety of metrics and KPIs that reflect both the efficiency of the testing process and the optimization of resources. Key metrics include environment availability, which measures the percentage of time test environments are available and operational when needed; setup and tear-down times, which assess how quickly environments can be prepared and decommissioned; defect discovery rates, to gauge the effectiveness of testing in identifying issues; and utilization rates, to understand how effectively the test environments are being used. Tracking the frequency and impact of environment-related defects can also provide insights into the stability and reliability of your test environments. Additionally, cost-related metrics, such as the cost per test hour, can help quantify the financial efficiency of your test environment management. By monitoring these metrics, organizations can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to enhance their TEM practices.
Q: Can you provide case studies or examples of organizations that successfully implemented Test Environment Management practices and the outcomes they achieved?
A: While the original article doesn’t provide specific case studies, many organizations across various industries have successfully implemented Test Environment Management practices with significant outcomes. For example, a large financial institution faced challenges with test environment conflicts and long setup times, leading to delays in their software release cycles. By adopting a more centralized TEM approach, implementing automated provisioning, and adopting containerization, they were able to reduce environment setup times from several days to just hours, significantly increasing their testing throughput and reducing time to market for new features. Another example is a software company that implemented a self-service portal for test environments, allowing developers and testers to spin up pre-configured environments on demand. This not only improved the efficiency of their testing process but also significantly reduced the workload on their IT operations team, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives. These examples demonstrate how effective TEM practices can lead to improved efficiency, faster time to market, and better resource utilization



One Response